Java-DAY3 - 程序流程控制、Random类
分支结构(if,switch)
实例:
public class IF {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int heart = 40;
if (heart < 60 || heart > 100) {
System.out.println("你的心跳数据:" + heart + " 需要检查");
}
System.out.println("检查结束");
///////////////////////////////////
double money = 100;
if (money >= 1300) {
System.out.println("成功");
} else {
System.out.println("你没钱了");
}
////////////////////////////
int score = 85;
if (score >= 0 && score < 60) {
System.out.println("C");
} else if (score >= 60 && score < 80) {
System.out.println("B");
} else if (score >= 80 && score < 90) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (score >= 90 && score < 100) {
System.out.println("A+");
}else {
System.out.println("分数不正确");
}
}
}
实例:
public class Switch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String weekday= "周四";
switch (weekday){
case "一":
System.out.println("A0");
break;
case "二":
System.out.println("B0");
break;
case "三":
System.out.println("C0");
break;
case "周四":
System.out.println("d0");
break;
case "周五":
System.out.println("e0");
break;
default:
System.out.println("错误");
}
}
}
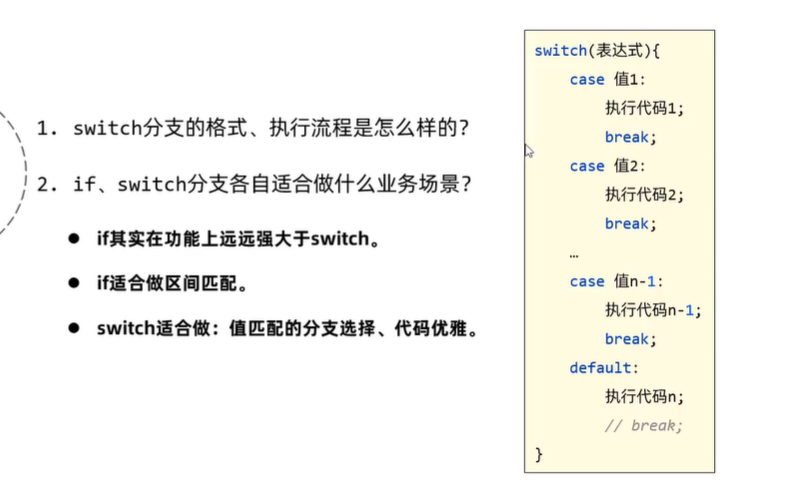
switch分支注意事项:
- 表达式类型只能是byte、short、int、char,JDK5开始支持枚举,JDK7开始支持String、不支持double、float、long。
- case给出的值不允许重复,且只能是字面量,不能是变量。
- 不要忘记写break,否则会出现穿透现象。
实例:
public class switch2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int month = 4;
switch (month){
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
System.out.println(month + "是31");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(month +"是29/28");
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
System.out.println(month + "是30");
break;
default:
System.out.println("有误");
}
}
}
什么情况下会出现switch穿透现象?
- case中没有写break。
switch穿透性能解决什么问题?
- 存在多个case分支的功能代码是一样时,可以用穿透性把流程集中到同一处处理,这样可以简化代码。
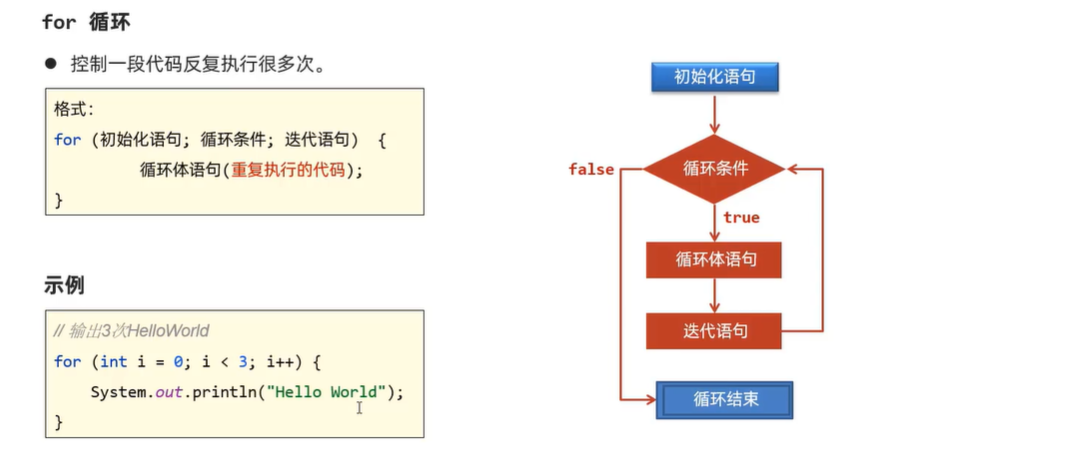
循环结构(for,while,do__while)
实例:
public class For {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 3; i++){
System.out.println("hello"); //输出三个“hello”:
}
}
}
实例:
int sum =0;
for (int i=1; i <= 5; i++){
sum +=i;
}
System.out.println("1~5的和:" + sum);
实例:
//第一种:在for循环中,通过if筛选
int sum2 =0;
for (int i=1; i <= 10; i+=2){
if (i % 2 == 1){
sum2 +=i;
}
}
System.out.println("1~10的奇数和:" + sum2);
//第二种方式 :直接for循环,在循环外定义一个整数变量sum用来累加这些数据。
int sum3 =0;
for (int i=1; i <= 10; i+=2){
sum3 +=i;
}
System.out.println("1~10的奇数和:" + sum3);
实例:
public class For_水仙花数 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count =0;
for (int i=100; i<=999;i++){
int ge=i % 10;
int shi=i / 10 % 10;
int bai=i / 100;
if((ge*ge*ge + shi*shi*shi + bai*bai*bai) == i){
System.out.println(i +"\t");
count++;
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("水仙花个数:" + count);
}
}
如何找出水仙花数?
- 定义一个for循环从“100一直到999”。
- 每次访问到数据后,提取该数据的:个位、十位、百位数字。
- 看各个数的立方和是否等于原数,等于则输出原数据。
如何计算出水仙花的个数?
- 在循环外定义一个变量count用于记录水仙花数。
- 每输出水仙花数时,让count++。
实例:
public class While {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i= 0;
while (i<3){
System.out.println("hello");
i++;
}
}
}
怎么解决此案例?
- 定义变量存储珠穆朗玛峰的高度、纸张的高度。
- 使用while循环,循环条件是(纸张厚度<山峰高度),内部控制纸张折叠,每折叠一次,纸张厚度
为原来两倍,循环外定义计数变量,每折叠依次让该变量+1
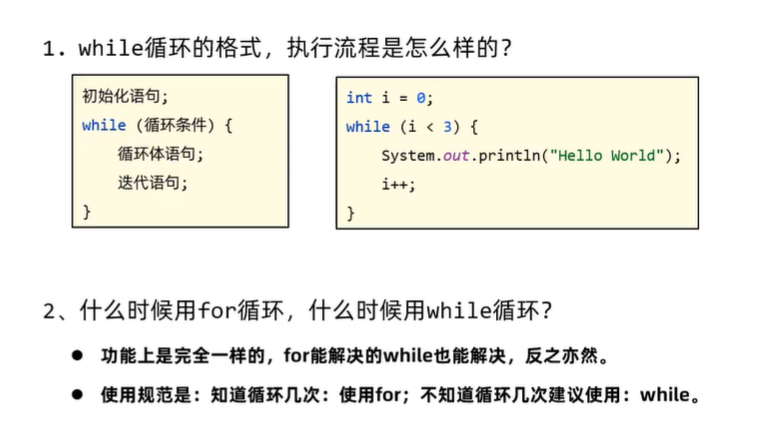
for和while使用总结
- 其实while能做的for都能实现;
- 但是如果一开始不知道循环次数的情况下,建议使用while循环解决更专业。
实例:
public class While {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i= 0;
while (i<3){
System.out.println("hello");
i++;
}
//珠穆朗玛峰
double height = 8848860;
double paper = 0.1;
int count =0;
while (paper <height){
paper *=2;
count++;
}
System.out.println("折叠次数:" +count); //折叠次数:27 ,厚度:1.34217728E7
System.out.println("厚度:" +paper);
}
}
实例:
public class DO_while {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=0;
do {
System.out.println("hello");
i++;
}while (i<3);
}
}
三种循环的区别(for,while,do__while)
- for循环和while循环(先判断后执行)
- do...while (第一次先执行后判断)
for和 while 的区别:
- for循环和while循环的执行流程是一模一样的。
- 如果已知循环次数建议使用for循环,如果不清楚要循环多少次建议使用while循环。
- for循环中,控制循环的变量只在循环中可以使用。While循环中,控制循环的变量在循环后还可以继续使用。
实例:
//死循环
while (true){
System.out.println("死循环");
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 密码案例 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//密码案例
int pass1=451;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.println("输入密码");
int pass2= sc.nextInt();
if (pass2 == pass1){
System.out.println("正确");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("错误");
}
}
}
}
实例:
public class 循环嵌套 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i= 0;i<5; i++){
for (int j=0;j<5;j++){
System.out.println("DK");
}
System.out.println("----------------");
}
}
}
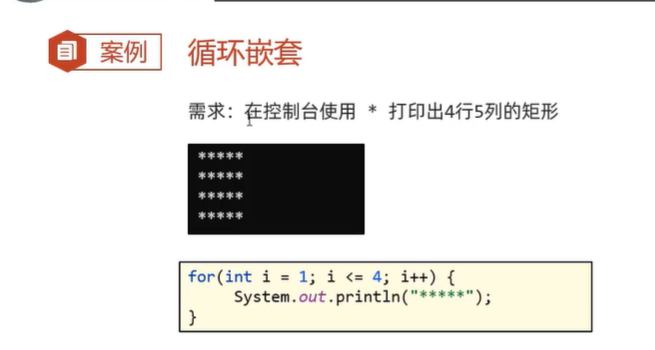
实例:
for (int i= 0;i<4; i++){
for (int j=0;j<5;j++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
跳转控制语句介绍
- break:跳出并结束当前所在循环的执行。
- continue:用于跳出当前循环的当次执行,进入下一次循环。
注意事项
- break :只能用于结束所在循环,或者结束所在switch分支的执行。
- continue :只能在循环中进行使用。
实例:
import java.util.Random;
public class random随机数 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r=new Random();
for (int i=0;i<20;i++){
int data= r.nextInt(10);
System.out.println(data);
}
System.out.println("-------------");
int data= r.nextInt(10) +1;
System.out.println(data);
int data1= r.nextInt(15) +3;
System.out.println(data1);
}
}
Random随机数类生成需要几步,具体是什么样的?
导包:import java.util.Random;- Random r= new Random();int number = r.nextIlnt(10);
Random随机数如何生成65 - 91之间的随机数?
- 65-91 => (o- 26)+65
- int number = r.nextInt(27)+65;
实例:
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 猜数字 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r=new Random();
int data= r.nextInt(100)+1;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.println("输入数据:");
int guess= sc.nextInt();
if (guess >data){
System.out.println("过大:");
}else if(guess <data){
System.out.println("过小:");
}else{
System.out.println("猜对了:");
break;
}
}
}
}














Comments | NOTHING